I've spent a lot of time trying to find a domesic manfacturer of security screws. I have found nothing.
But..
My friend gave me link to a large distributor of fasteners and another equipment.
I had called them and met then. They showed me one catalog of German manufacturer. Its REYHER http://www.reyher.de/en/company
I was happy to find there what I was looking for a long time.
It's Secure Torx:
And this is Snake eyes:
I've sent request to get a proposal. I'll write here how much does it cost.
kreyda
Wednesday, May 13, 2015
Tuesday, March 3, 2015
Security screw in domestic RFID readers
To be honest I haven't found any domestic RFID readers which have a security screw yet.
Monday, March 2, 2015
ACS - The BEST PRACTICE compilation from the HID
How many green stars have you got for your access control system?
Send me a letter, if you want to have the original XMIND-file.
Sunday, March 1, 2015
Wiegand interface. Chance to live?
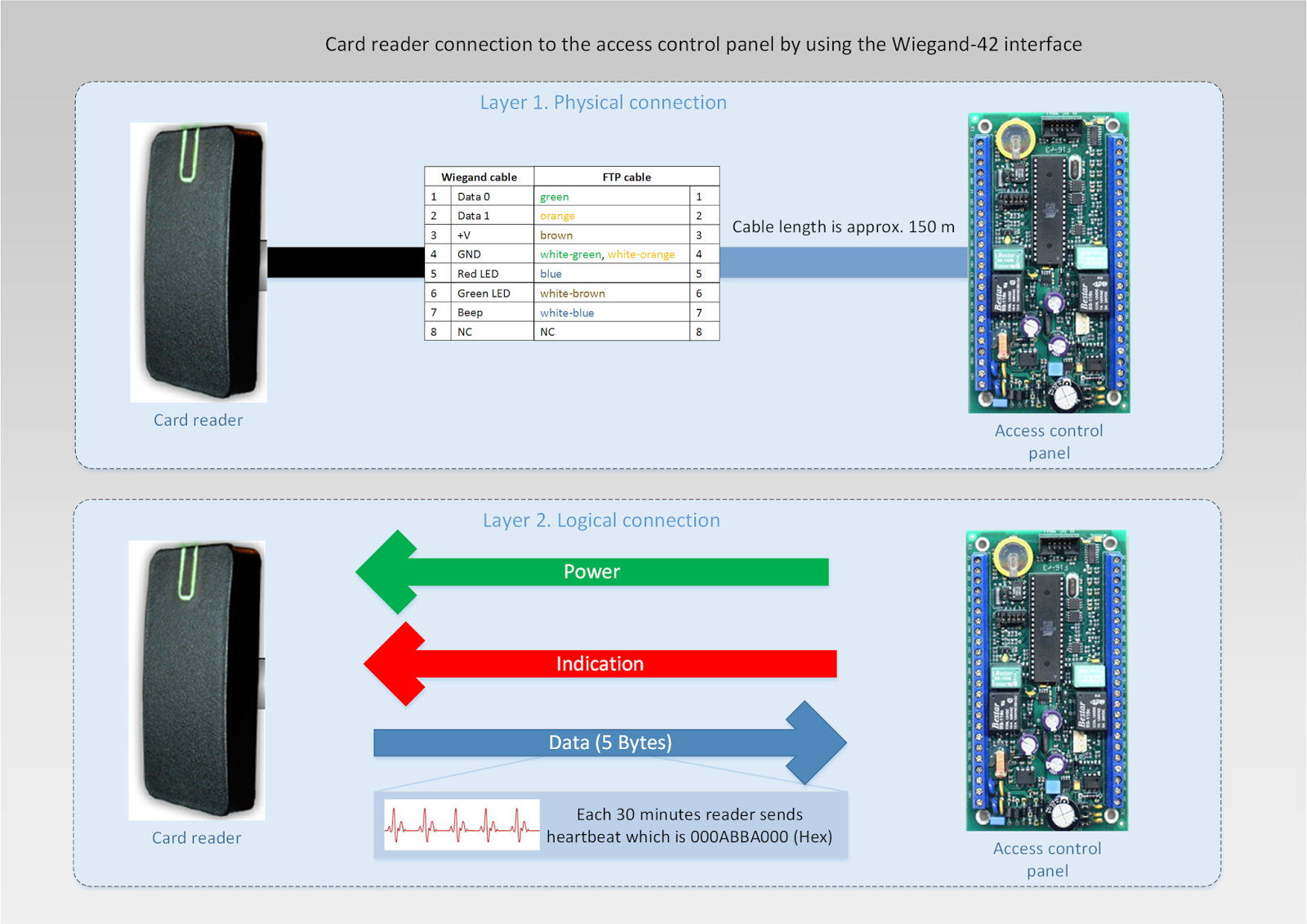
A Wiegand interface is the most popular interface between RFID-reader and access control panel.
This legacy interface has many modifications but the one thing that is important: how many bytes a reader will send to the access control panel. It could be 3 bytes (Wiegand-26), 5 bytes (Wiegand-42) and even 7 bytes.
The most popular Wiegand interface is 26. And by getting just 3 bytes from the reader wouldn't be enough to have a strong security access control system. Many domestic manufacturers (and even foreign ones) have still produced RFID-readers with just one Wiegand-26 interface unfortunately. Thanks goodness there is one domestic vendor which has programmable readers. Their interface can be set up as Wiegand-42, so reader can send 5 bytes of code to the access panel.
Some installers don’t pay attention to the physical connection between reader and access panel. According to the reader's manual the right cable has to be selected. The FTP-cable would be the right choice. Wiegand's DATA lines have to be connected with the different twisted pairs (1 and 2). Their free twisted pairs have to be connected to the ground line (4).
The Wiegand interface is unidirectional. It means that data is transfered in one direction only: from reader to the access panel. So access panel waits for a code on the line. If code is absent it means that there is no card near the reader or the reader is dead or the line is corrupted. To solve this problem in this way I asked one vendor to make a new firmware for its reader and now it sends each half an hour a "heart beat" code. The access panel by getting this code generates DENY sound via reader's BEEP line. To mute this noisy and confusing sound, the reader disables its BEEP line for a few seconds after heart beat code has been sent.
I love Swedish pop group ABBA and that code is 000ABBA000 (Hex). ACS log analyzer operates with this code and informs Security Officer in case of troubles with it.
As I said before Wiegand interface is obsolete. Nowadays the new, secure and reliable protocol has been introduced. It is OSDP. I hope many worldwide access control vendors will support it.
Location:
Kyiv city, Ukraine
Saturday, February 28, 2015
If you have an Access Control System does it mean that your assets are in safe? Well..it depends..
I began to study Access Control Systems (ACS) a year ago. Since
then I have gained enough knowledge to say that we have lots of problems in this
area!
Access cards
Weakness of a chain depends on the weakness of one cell. In the "ACS chain" we have many "cells" and the weakest is the 125 kHz card (EM-Marin, Indala, etc.).
The reason is that this type of cards can be easily cloned. Nowadays in Ukraine you can clone it everywhere and it costs just a few dollars. A service man can even arrive to your office or home.
Ads in Odesa
I've cloned a few pass cards, checked them and have to say that they work perfectly.
I have visited many business centers in Kyiv,"secured" by EM-Marin cards, and took a photos of numbers these cards:
Access cards
Weakness of a chain depends on the weakness of one cell. In the "ACS chain" we have many "cells" and the weakest is the 125 kHz card (EM-Marin, Indala, etc.).
The reason is that this type of cards can be easily cloned. Nowadays in Ukraine you can clone it everywhere and it costs just a few dollars. A service man can even arrive to your office or home.
Ads in Odesa
Ads in Kyiv
I've cloned a few pass cards, checked them and have to say that they work perfectly.
I have visited many business centers in Kyiv,"secured" by EM-Marin cards, and took a photos of numbers these cards:
After
that you can call to a service man and clone those cards by using many
devices, such as KeyMaster3RF for
instance.
Information from EM-Marin proximity card can be even grabbed remotely by using a special portable RF-reader. Distance for reading a card's number can be up to 1 meter.
This problem can be solved by using a smart card instead of a proximity card. One of the well-known smart cards is Mifare card. This card works on the 13 MHz and has a chip with memory inside. The most popular Mifare card is Classic 1k and it has 1kB memory.
By using opportunity to work with memory of the smart card we can make it secure.
We can write a token inside the card memory and secure it with the Mifare key. Just that card reader which knows the Mifare key can read the token and then send it to an access panel.
This solution can prevent the main problem of ACS - card cloning.
Despite that even Mifare Classic cards have vulnerability. Some of them are solved by writing data in ALL SECTORS, some of them are mitigated by using other security measurements like CCTV, logging and employees awareness.
Nevertheless, many companies have still used EM-Marin cards as the pass cards for its employees. The main problem is in the heritage.
Companies use tenant facilities from their landlords and have to use the legacy ACS equipment for its own purposes.
But solution exists: it's a trendy NFC (Near-Field Communication) card.
Some NFC cards have the same Mifare Classic 1k chip and look like labels with the glued surface.
Legacy EM-Marin pass card can be easily upgraded to the "sandwich card".
At the moment I have found just one domestic vendor which can work with memory sectors of Mifare cards. Unfortunately many foreign companies are stuck on the EM-Marin phase. That's a shame. I hope this situation will change in the future.
Information from EM-Marin proximity card can be even grabbed remotely by using a special portable RF-reader. Distance for reading a card's number can be up to 1 meter.
This problem can be solved by using a smart card instead of a proximity card. One of the well-known smart cards is Mifare card. This card works on the 13 MHz and has a chip with memory inside. The most popular Mifare card is Classic 1k and it has 1kB memory.
By using opportunity to work with memory of the smart card we can make it secure.
We can write a token inside the card memory and secure it with the Mifare key. Just that card reader which knows the Mifare key can read the token and then send it to an access panel.
This solution can prevent the main problem of ACS - card cloning.
Despite that even Mifare Classic cards have vulnerability. Some of them are solved by writing data in ALL SECTORS, some of them are mitigated by using other security measurements like CCTV, logging and employees awareness.
Nevertheless, many companies have still used EM-Marin cards as the pass cards for its employees. The main problem is in the heritage.
Companies use tenant facilities from their landlords and have to use the legacy ACS equipment for its own purposes.
But solution exists: it's a trendy NFC (Near-Field Communication) card.
Some NFC cards have the same Mifare Classic 1k chip and look like labels with the glued surface.
Legacy EM-Marin pass card can be easily upgraded to the "sandwich card".
After that a tenant can update its own ACS equipment
(card readers) and implement the Mifare technology inside the company.
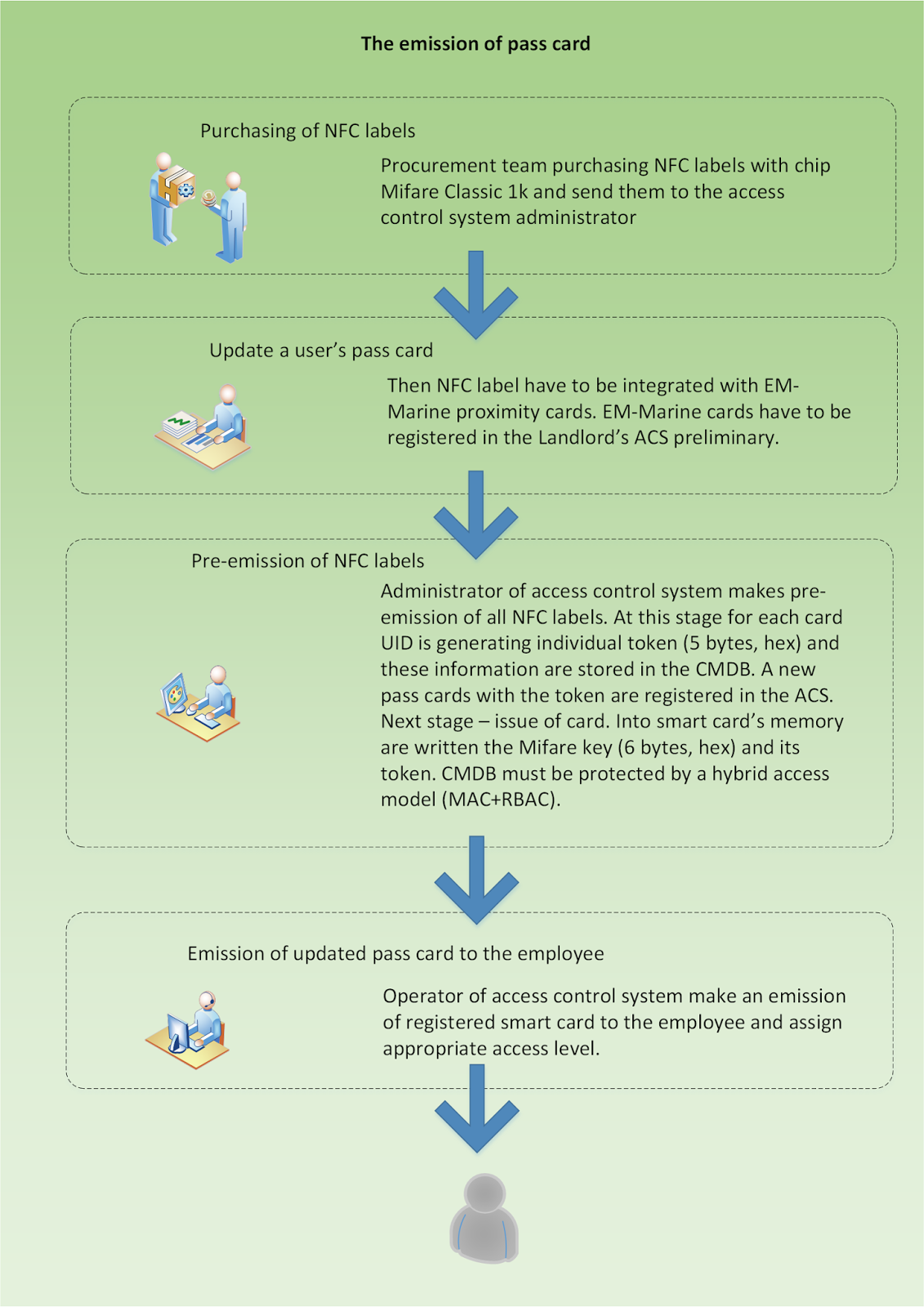
This means that two-stage process has to be implemented:
1. Pre-emission of cards.
2. Emission of cards.
At this stage an additional control (security operation)
would be great to implement as separation of duties. This control additionally
mitigates the risk of getting unauthorized access to the company's
premises by separation of operations between two employees. One operator cannot
perform operations without another one and vice versa.
At the moment I have found just one domestic vendor which can work with memory sectors of Mifare cards. Unfortunately many foreign companies are stuck on the EM-Marin phase. That's a shame. I hope this situation will change in the future.
Location:
Kyiv, Kyiv city, Ukraine
Friday, March 28, 2014
Trouble to copy a large file from a Checkpoint SPLAT system to a backup host using WinSCP
On of the main task of a responsible security engineer is regulary make a backup of its system.
As soon as I finish
making a backup procedure of my Security Management server I've tried to copy
that file (its size is almost 300 MB) using a program WinSCP which a newest
version at that moment is 5.5.1
Copying it I've
faced with a window that informs me that unexpectedly error has happened. After
that my session was disconnected.
Somewhere in the net
I read about this trouble and people recommended to use a lower version of
WinSCP. I've decided to try
a different version of it. Lots of my attempts were not succeed until I closed
to a version 4.0.3
And it works!
The
file was successfully copied to my backup host.
Monday, September 2, 2013
Where is located the main.cf file in the Trend Micro InterScan Messaging Security Virtual Appliance v.8.5
After installation the new mail gateway IMSVA 8.5 I've noticed that some mail servers have rejected my messages with the next logs:
host [X.X.X.X] said: 550 5.7.1 >: Helo command rejected: Host not found (in reply to
RCPT TO command)
I thought there is problem with PTR-record, but it's OK. My mate helped me to find the main reason.
Problem occurs because my IMSVA uses its own hostname for invitation with other mail servers and this hostname is different from hostname registered for its MX-record.
For example:
Hostname imsva85.domain.com
MX-record smtp2.domain.com
There is two way to solve this problem - change hostname or find solution inside mail service.
I decided to leave internal hostname and tried to find another way.
As all probably know IMSVA based on the POSTFIX system. I'd installed and managed the postfix systems few year ago and this experience helped me. But I couldn't find postfix's files in the ordinary folder /etc/postfix. I've connected with WinSCP and searched the main.cf file. File was found here /opt/trend/imss/postfix/etc/postfix
Original part of this file described bellow:
host
I thought there is problem with PTR-record, but it's OK. My mate helped me to find the main reason.
Problem occurs because my IMSVA uses its own hostname for invitation with other mail servers and this hostname is different from hostname registered for its MX-record.
For example:
Hostname imsva85.domain.com
MX-record smtp2.domain.com
There is two way to solve this problem - change hostname or find solution inside mail service.
I decided to leave internal hostname and tried to find another way.
As all probably know IMSVA based on the POSTFIX system. I'd installed and managed the postfix systems few year ago and this experience helped me. But I couldn't find postfix's files in the ordinary folder /etc/postfix. I've connected with WinSCP and searched the main.cf file. File was found here /opt/trend/imss/postfix/etc/postfix
Original part of this file described bellow:
#
INTERNET HOST AND DOMAIN NAMES
#
# The
myhostname parameter specifies the internet hostname of this
# mail
system. The default is to use the fully-qualified domain name
# from
gethostname(). $myhostname is used as a default value for many
# other
configuration parameters.
#
#myhostname
= host.domain.tld
#myhostname
= virtual.domain.tld
# The
mydomain parameter specifies the local internet domain name.
# The
default is to use $myhostname minus the first component.
#
$mydomain is used as a default value for many other configuration
#
parameters.
#
#mydomain
= domain.tld
I've added one string about the MX-record, and now this part looks like this:
#
INTERNET HOST AND DOMAIN NAMES
#
# The
myhostname parameter specifies the internet hostname of this
# mail
system. The default is to use the fully-qualified domain name
# from
gethostname(). $myhostname is used as a default value for many
# other
configuration parameters.
#
#myhostname
= host.domain.tld
#myhostname
= virtual.domain.tld
myhostname = smtp2.domain.com
After that file main.cf was saved and virtual server was stopped through CLI-mode.
After restarting mail service works perfectly and problem is gone.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)